Exploring the 3 layers of software interactions (APIs)
Posted by: Prerna | May 19, 2024
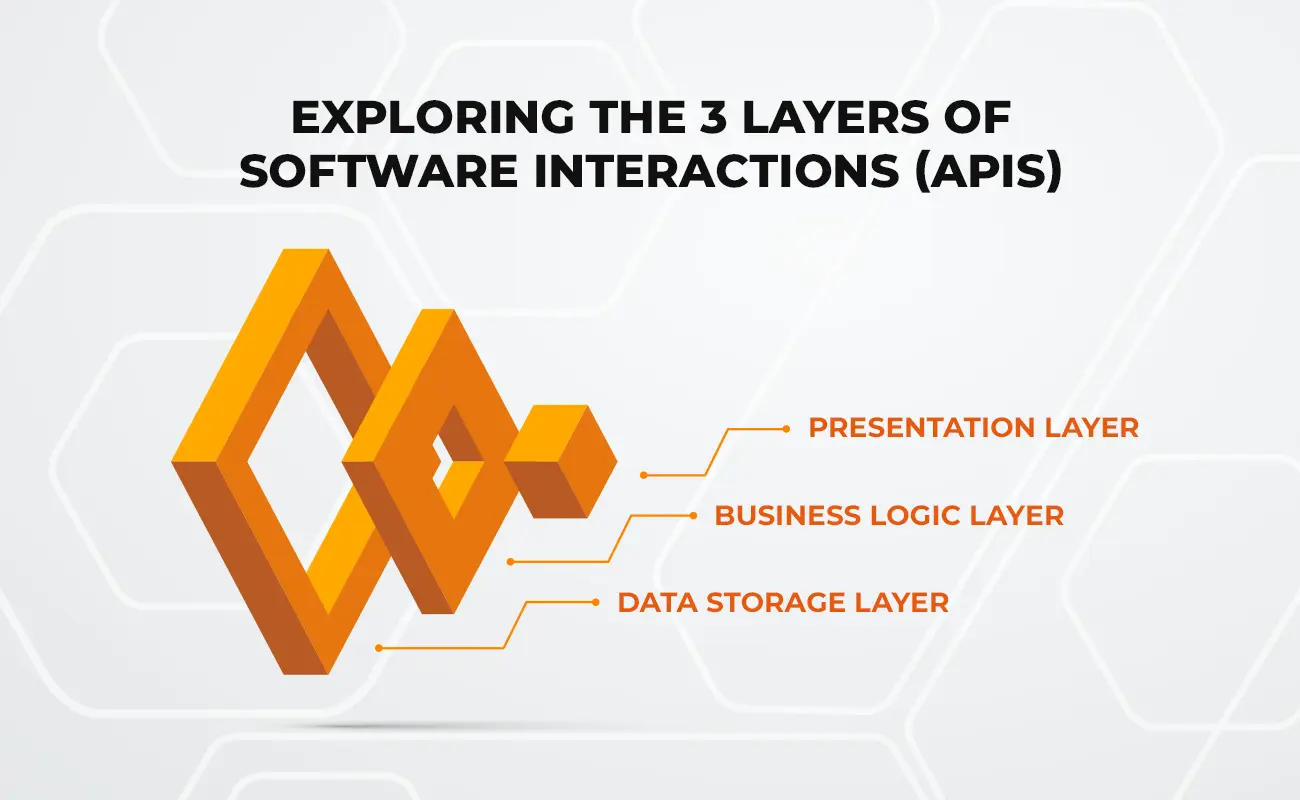
Categories: API, Presentation Layer, Business Logic Layer, Data Storage Layer
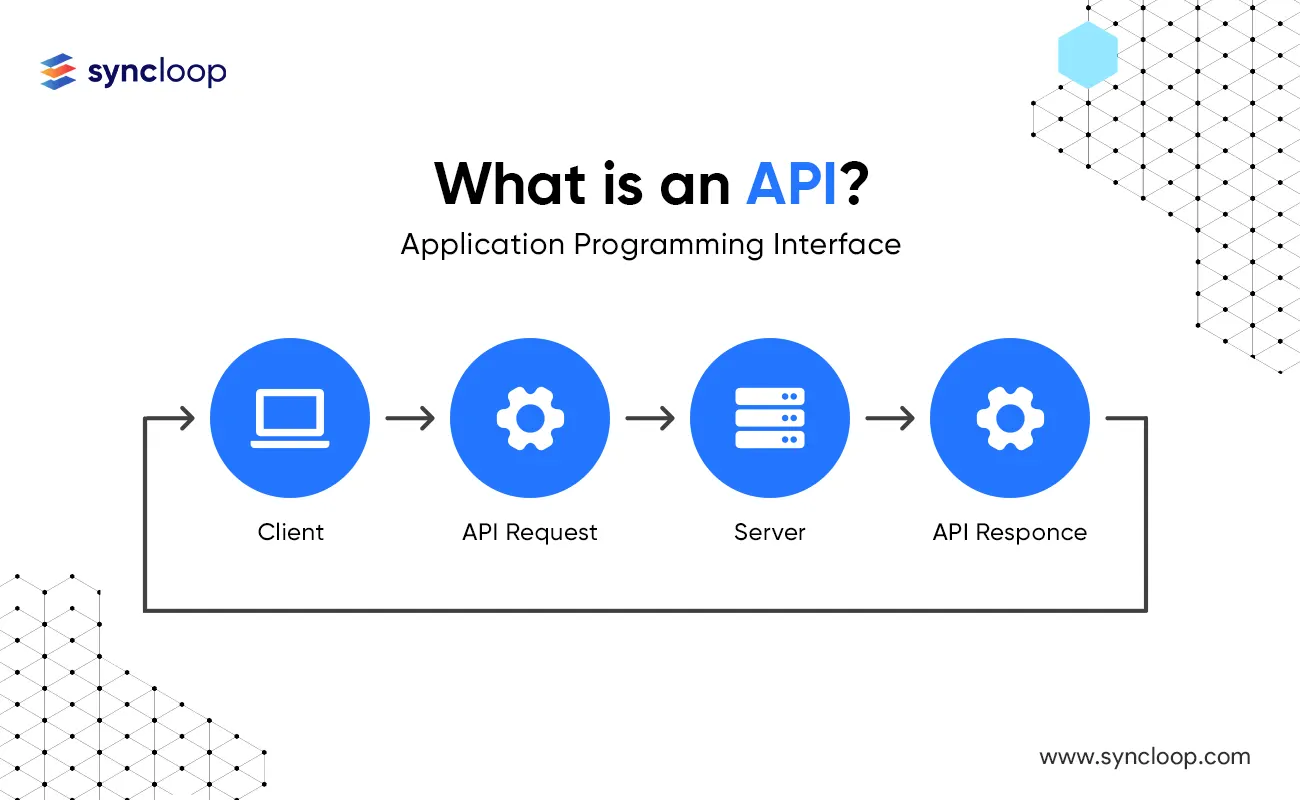
Application Programming Interfaces, commonly known as APIs, are a set of protocols, routines, and tools that enable software applications to interact with each other. They allow different software applications to exchange information seamlessly and efficiently.
APIs have become increasingly important in today's digital world, as they enable developers to build powerful applications that can connect with other services and platforms. APIs can be broken down into three different layers, each of which serves a different purpose.
In this blog post, we will explore the three layers of APIs and what they do.
1. Presentation Layer
The presentation layer, also known as the "API endpoint," is the layer that developers interact with most frequently. This layer provides a user-friendly interface for developers to access the functionality and data of the underlying service. It is responsible for processing incoming requests and returning responses in a format that developers can easily understand.
The presentation layer can take many different forms, depending on the requirements of the API. It could be a REST API that uses HTTP requests to exchange data or a SOAP API that uses XML messages to communicate. Regardless of the specific implementation, the presentation layer is the public-facing aspect of the API and is the first point of contact for developers.
2. Business Logic Layer
The business logic layer, also known as the "API middleware," is the layer that contains the core logic of the API. It is responsible for processing the requests received from the presentation layer and generating responses based on the requested actions.
The business logic layer is where the API's core functionality resides. It may perform data validation, authentication and authorization, database queries, or other complex operations. This layer is typically developed by the service provider and is not exposed directly to developers.
3. Data Storage Layer
The data storage layer, also known as the "API database," is the layer where all of the data used by the API is stored. This layer is responsible for managing data storage, retrieval, and modification. It may use a variety of database technologies such as SQL, NoSQL, or object-oriented databases.
The data storage layer is the most critical component of the API since it holds the data that the API relies on. If the data storage layer fails, the entire API may fail. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the data storage layer is designed and implemented correctly.
In conclusion, APIs consist of three layers: presentation layer, business logic layer, and data storage layer. Each layer plays a crucial role in the API's functionality and performance. Understanding the three layers of an API is essential for developers looking to build robust, reliable, and scalable APIs.
Back to Blogs